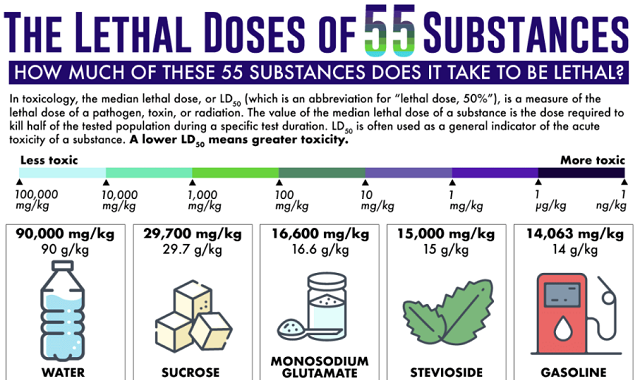
There are certain everyday substances that can be toxic to animals and humans depending on the amount of exposure. Water for example can become toxic in the body if there is too much. There are also other chemicals, pharmaceuticals, toxins, pathogens and animal venoms that can be toxic to humans in very small doses. This measurement of toxicity is known as the median lethal dose. Keep in mind however the LD50, as it is also known as, is not the lethal dose for all subjects. Some may be killed by much less, while others survive doses far higher than the LD50.
There are certain everyday substances that can be toxic to animals and humans depending on the amount of exposure. Water for example can become toxic in the body if there is too much. There are also other chemicals, pharmaceuticals, toxins, pathogens and animal venoms that can be toxic to humans in very small doses. This measurement of toxicity is known as the median lethal dose. Keep in mind however the LD50, as it is also known as, is not the lethal dose for all subjects. Some may be killed by much less, while others survive doses far higher than the LD50.
Hydrogen is a small element but a powerful tool that is used for conserving and creating energy. Hydrogen is one of the most important gases for commercial use. There are tons of uses for hydrogen such as powering many energy plants. Hydrogen has been used in the industrial and chemical processes for decades now, and it has proven to be a great resource.
Hydrogen holds significant importance in the energy industry. It is of great market value at the moment. We all are looking forward to a low-carbon energy future due to the deteriorating condition of our environment. Hydrogen potentially contains and is heavily considered an answer to low-carbon future. It can help decarbonize many departments, from vehicles to chemical factories.
Do you know what's in the food you eat? Millions of Americans put their trust in organizations such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) to determine which foods are safe and which aren't for human consumption but if you look at the issue from a global scale you will begin to notice that many additives and chemicals in our food have actually been banned in many countries around the world. Arguments can be made for both sides. One side might say, "There isn't enough evidence to prove they are dangerous." while the other would proclaim "It's better to be safe than sorry!" Regardless of which side of the fence you stand on, it's still important to know that there are so many chemicals being consumed by humans every day that some believe to be dangerous. This infographic from YourLawyer.com examines 12 of the most famous!
World history is interwoven with tragic threads of materials, chemicals, and products gone wrong, exposing the public and the environment to colossal harm. Sometimes this is due to oversights in research and unpredictable outcomes. After all, hindsight is 20/20. However, there have been many cases of companies actively suppressing damaging information from reaching the public for the sake of profit and reputation.
For example, the tobacco industry paid “merchants of doubt” doctors and scientists to deliberately obfuscate the truth about the dangers of cigarettes to health. Another example is the horrifying and tragic saga of the “Radium Girls”. Between 1917 and 1926, around 4,000 workers were told that the glowing paint used for watch dials was harmless and were encouraged to lick their paint brushes to create a fine point.
These “radium girls” suffered horrendous effects from radium exposure, such as anemia, bone fractures, necrosis of the jaw, and death. Some victims were so contaminated that radiation can be detected above their graves. This infographic from YourLawyer.com explores 20 materials that we discovered too late (by ignorance or deception) were hazardous to health and the environment.
Due to mounting evidence of its health benefits, it is increasingly used as a key ingredient in consumer packaged goods such as food, beverages, and health and wellness products. This burgeoning market is estimated to grow from $5 billion in 2019, to $23.7 billion by 2023. However, major challenges with existing products need to be addressed, such as poor bioavailability, or the rate at which CBD is absorbed into the bloodstream.
When CBD is extracted from the cannabis plant, it takes an oil-based form. Like any oil, it is hydrophobic, meaning it will not dissolve in water. As a result, CBD oil resists absorption into the bloodstream—with 96% of it being flushed from the body without ever having an active effect. Nanoemulsion is the most common method of creating CBD-infused products. The process involves pulverizing cannabinoids into nano-sizes, and combining them with an emulsifier and a carrier oil, in an attempt to create a water-soluble CBD.
Each and every one of us has a ‘chemical load’ – the number of toxins we carry in our bodies, which can include heavy metals like mercury, lead or arsenic, and PBDEs (Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers) such as phthalates, formaldehyde, bis phenol A and PCBs (Polychlorinated Biphenyls).
Your chemical load can have a profound impact on your health – heavy metals are extremely detrimental to your neurological functioning, phthalates can disrupt your endocrine balance and lead to hormonal dysfunction, and other PBDEs can seriously impair the functioning of your thyroid gland. Read more about endocrine disruptors and how they affect your health.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)